Maintaining Scheduled GitHub Actions Alive
The Keep Alive action is a utility that prevents GitHub repositories from becoming inactive by creating an empty commit and pushing it to the repository. This is particularly useful for maintaining GitHub Actions with scheduled triggers, which GitHub automatically disables after 60 days of repository inactivity.
How It Works
The action performs these steps:
- Checks out the repository
- Configures a local git user as "Keepalive"
- Creates an empty commit with the message "Keeping the repository alive"
- Pushes the commit to the repository
Usage
The most effective way to implement the Keep Alive pattern is by creating a scheduled workflow that:
- Runs on a regular schedule (e.g., daily)
- Checks how much time has passed since the last commit
- Invoke the
Keep Aliveaction and creates an empty commit only when necessary (approaching the 60-day limit)
Implementation Example
Here is a complete example of a Keep Alive workflow:
name: Keep Alive
on:
workflow_dispatch:
schedule:
- cron: "0 0 * * *" # Run at 00:00 every day
jobs:
keep_alive:
runs-on: "ubuntu-latest"
permissions:
contents: write
actions: write
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Calculate days since last commit
id: commit_date
run: |
# Calculate days since last activity
LAST_COMMIT_DATE=$(git log -1 --format=%ct)
CURRENT_DATE=$(date +%s)
DIFFERENCE=$(( ($CURRENT_DATE - $LAST_COMMIT_DATE) / 86400 ))
echo "days_since_commit=$DIFFERENCE" >> $GITHUB_ENV
# Use the Keep Alive action when needed
- name: Keep Alive
if: env.days_since_commit >= '55'
uses: pagopa/dx/.github/actions/keep-alive@main
with:
bot_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_BOT_TOKEN }}
Adapting This Workflow
When implementing this pattern in your own repositories:
- Adjust the threshold - The 55-day threshold can be modified based on your specific needs
- Consider the schedule - The daily check frequency can be adjusted
- Configure the secret - Create a personal access token with repository
write permissions and store it as a repository secret (e.g.,
GITHUB_BOT_TOKEN), then pass it to thebot_tokeninput - Ensure proper permissions:
- The workflow requires
contents: writeto push commits - Enable
Read and Write permissionsfor workflows inside repository settings - If your repository uses branch protection with required pull requests, configure "Allow specified actors to bypass required pull requests" by adding the GitHub account that corresponds to the token passed to the action
- The workflow requires
The action uses bot_token to make empty commits to the repository. It's
recommended to create a Personal Access Token (PAT) using a bot account (such as
dx-pagopa-bot) and add it as a secret to pass to the action. Note that the
chosen bot account must be added to the list of pull request bypassers
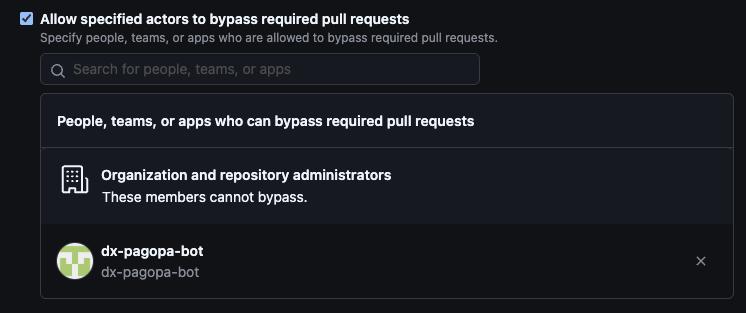 otherwise, it won't be able
If the bot account is not visible in the list of bypasses, ensure it has been
added as a collaborator to the repository.
otherwise, it won't be able
If the bot account is not visible in the list of bypasses, ensure it has been
added as a collaborator to the repository.